A quick-reference guide, with examples, on how to add math notation to Markdown documents.
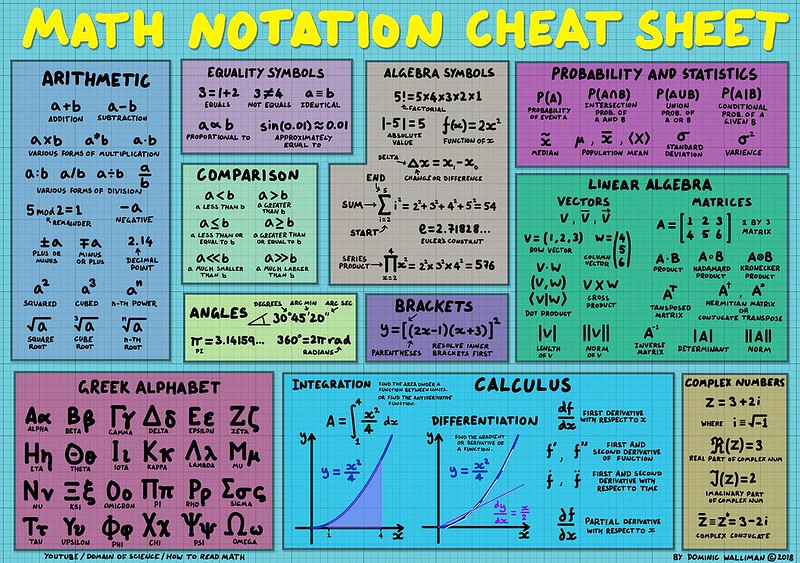
The scope of mathematical notation included in this cheat sheet is drawn from the Math Notation Cheat Sheet poster, created by Dominic Walliman , included here with permission. The associated YouTube video, which is excellent, is The Map of Mathematics .
Including Math Notation in Markdown
There are two ways to include math notation in Markdown. First, inline, which means that the notation is included in the paragraph or sentence, with the flow of text.
The second is as separate code blocks, so that the notation is shown in it’s own paragraph.
Inline math notation is wrapped in single-dollar signs. For example, for the square of "x", just type $x^2$, which is then formatted as $x^2$. This is $\LaTeX$ notation.
Alternatively, code blocks of $\LaTeX$ begin and end with two dollar signs, wrapped inside triple backticks. For example…
1```
2$$
3\displaystyle\sum_{k=3}^5 k^2=3^2 + 4^2 + 5^2 =50
4$$
5```
The above is rendered as:
$$ \displaystyle\sum_{k=3}^5 k^2=3^2 + 4^2 + 5^2=50 $$
LaTeX Cheat Sheet
Tip: These tables are wide, so you may need to scroll horizontally to see all the columns, or rotate your phone to landscape.
Arithmetic
| Notation | Example | Inline | Code Block |
|---|---|---|---|
| Addition | $a+b$ | $a+b$ | $$a+b$$ |
| Subtraction | $a-b$ | $a-b$ | $$a-b$$ |
| Various Forms of Multiplication | $a \times b$ $a \ast b$ $a \cdot b$ | $a \times b$$a \ast b$$a \cdot b$ | $$a \cdot b$$ |
| Various Forms of Division | $a \colon b$ $a / b$ $a \div b$ $\frac{a}{b}$ | $a \colon b$$a / b$$a \div b$$\frac{a}{b}$ | $$a \div b$$ |
| Remainder / Modulo | $5 \mod 2 = 1$ | $5\mod 2=1$ | $$5\mod 2=1$$ |
| Negative Value | $-a$ | $-a$ | $$-a$$ |
| Plus or Minus, Minus or Plus | $\pm a$ $\mp a$ | $\pm a$$\mp a$ | $$\pm a$$ |
| Squared, Cubed, nth-Power | $a^2$ $a^3$ $a^n$ | $a^2$$a^3$$a^n$ | $$a^3$$ |
| Square Root, Cube Root, nth-Root | $\sqrt{a}$ $\sqrt[3]{a}$ $\sqrt[n]{a}$ | $\sqrt{a}$$\sqrt[3]{a}$$\sqrt[n]{a}$ | $$\sqrt[3]{a}$$ |
Equality
| Notation | Example | Inline | Code Block |
|---|---|---|---|
| Equals | $3=1+2$ | $3=1+2$ | $$3=1+2$$ |
| Not Equals | $3 \neq 4$ | $3\neq4$ | $$3\neq4$$ |
| Identical / Equivalent To | $a \equiv b$ | $a \equiv b$ | $$a \equiv b$$ |
| Proportional To | $a \propto b$ | $a \propto b$ | $$a \propto b$$ |
| Approximately Equal To | $\sin(0.01) \approx 0.01$ | $\sin(0.01) \approx 0.01$ | $$\sin(0.01) \approx 0.01$$ |
Comparison
| Notation | Example | Inline | Code Block |
|---|---|---|---|
| a Less Than b a Greater Than b | $a < b$ $a > b$ | $a<b$$a>b$ | $$a<b$$ |
| a Less Than or Equal To b a Greater Than or Equal To b | $a \leq b$ $a \geq b$ | $a \leq b$$a \geq b$ | $$a \leq b$$ |
| a Much Smaller Than b a Much Larger Than b | $a \ll b$ $a \gg b$ | $a \ll b$$a \gg b$ | $$a \ll b$$ |
Algebra
| Notation | Example | Inline | Code Block |
|---|---|---|---|
| Factorial | $5 ! = 5 \times 4 \times 3 \times 2 \times 1$ | $5!=5 \times 4 \times 3 \times 2 \times 1$ | $$5!=5 \times 4 \times 3 \times 2 \times 1$$ |
| Absolute Value | $| -5 | = 5$ | $|-5|=5$ | $$|-5|=5$$ |
| Function Of | $f(x) = 2x^2$ | $f(x)=2x^2$ | $$f(x)=2x^2$$ |
| Change or Difference | $\Delta x = x_1 - x_0$ | $\Delta x = x_1 - x_0$ | $$\Delta x = x_1 - x_0$$ |
| Pi | $\pi = 3.14159…$ | $\pi = 3.14159...$ | $$\pi$$ |
| Euler’s Constant | $e = 2.71828…$ | $e = 2.71828...$ | $$e = 2.71828...$$ |
| Sum | $\displaystyle\sum_{k=3}^5 k^2 = 3^2 + 4^2 + 5^2 = 50$ | $\displaystyle\sum_{k=3}^5 k^2=3^2 + 4^2 + 5^2 =50$ | $$\displaystyle\sum_{k=3}^5 k^2=3^2 + 4^2 + 5^2 =50$$ |
| Series Product | $\displaystyle\prod_{x=2}^4 x^2 = 2^2 \times 3^2 \times 4^2 = 576$ | $\displaystyle\prod_{x=2}^4 x^2 = 2^2 \times 3^2 \times 4^2 = 576$ | $$\displaystyle\sum_{k=2}^4 k^2=2^2 \times 3^2 \times 4^2 = 576$$ |
| Brackets & Parentheses | $[\ldots]$ $(\ldots)$ | $[\ldots] (\ldots)$ | $$[\ldots] (\ldots)$$ |
Angles
| Notation | Example | Inline | Code Block |
|---|---|---|---|
| Angle | $\angle$ | $\angle$ | $$\angle$$ |
| Degree, Arc Min, Arc Sec | $30\degree45\rq30\rq\rq$ | $30\degree45\rq30\rq\rq$ | $$30\degree45\rq30\rq\rq$$ |
| Radians | $360\degree = 2\pi rad$ | $360\degree = 2\pi rad$ | $$360\degree = 2\pi rad$$ |
Probability & Statistics
| Notation | Example | Inline | Code Block |
|---|---|---|---|
| Probability of Event A | $P(A)$ or $\Pr(A)$ | $P(A)$ or $\Pr(A)$ | $$P(A)$$ |
| Intersection Prob. of A & B | $P(A \cap B)$ | $P(A \cap B)$ | $$P(A \ca pB)$$ |
| Union Prob. of A or B | $P(A \cup B)$ | $P(A \cup B)$ | $$P(A \cup B)$$ |
| Conditional Prob. of A Given B | $P(A | B)$ | $P(A|B)$ | $$P(A|B)$$ |
| Median | $\tilde{x}$ | $\tilde{x}$ | $$\tilde{x}$$ |
| Population Mean | $\mu , \overline{x} , \langle x \rangle$ | $\mu , \overline{x} , \langle x \rangle$ | $$\mu , \overline{x} , \langle x \rangle$$ |
| Standard Deviation | $\sigma$ | $\sigma$ | $$\sigma$$ |
| Varience | $\sigma^2$ | $\sigma^2$ | $$\sigma^2$$ |
Linear Algebra
Linear Algebra: Vectors
| Notation | Example | Inline | Code Block |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vectors | $\mathbf{v} \overline{v} \vec{v}$ | $\mathbf{v}\overline{v}\vec{v}$ | $$\mathbf{v} \overline{v} \vec{v}$$ |
| Row Vector | $v = \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 2 & 3 \end{pmatrix}$ | $v=\begin{pmatrix}1&2&3\end{pmatrix}$ | $$v = \begin{pmatrix}1 & 2 & 3\end{pmatrix}$$ |
| Column Vector | $w = \begin{pmatrix} 4 \cr 5 \cr 6 \cr \end{pmatrix}$ | $w=\begin{pmatrix}4\cr5\cr6\cr\end{pmatrix}$ | $$w=\begin{pmatrix}4 \cr5 \cr6 \cr\end{pmatrix}$$ |
| Dot Product | $\mathbf{v} \cdot \mathbf{w}$ $(v,w)$ $\left< v|w \right>$ | $\mathbf{v} \cdot \mathbf{w}$<br>$(v,w)$<br>$\left<v | w\right>$ | $$\mathbf{v}\cdot\mathbf{w}(v,w)\left<v|w \right>$$ |
| Cross Product | $v \times w$ | $v \times w$ | $$v \times w$$ |
| Length of v | $|v|$ | $|v|$ | $$|v|$$ |
| Norm of v | $||v||$ | $||v||$ | $$||v||$$ |
Linear Algebra: Matrices
| Notation | Example | Inline | Code Block |
|---|---|---|---|
| Matrix, 2 By 3 | $A=\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 2 & 3 \cr 4 & 5 & 6 \end{bmatrix}$ | $A=\begin{bmatrix}1&2&3\cr4&5&6\end{bmatrix}$ | $$A=\begin{bmatrix}1 & 2 & 3 \cr4 & 5 & 6\end{bmatrix}$$ |
| Product | $A \cdot B$ | $A \cdot B$ | $$A \cdot B$$ |
| Hadamard Product | $A \circ B$ | $A \circ B$ | $$A \circ B$$ |
| Kronecker Product | $A \otimes B$ | $A \otimes B$ | $$A \otimes B$$ |
| Transposed Matrix | $A^T$ | $A^T$ | $$A^T$$ |
| Hermitian Matrix or Conjugate Transpose | $A^\dag$ $A^\ast$ | $A^\dag$$A^\ast$ | $$A^\dagA^\ast$$ |
| Inverse Matrix | $A^{-1}$ | $A^{-1}$ | $$A^{-1}$$ |
| Determinant | $|A|$ | $|A|$ | $$|A|$$ |
| Norm | $||A||$ | $||A||$ | $$||A||$$ |
Calculus
| Notation | Example | Inline | Code Block |
|---|---|---|---|
| Example Function: $y = \frac{x^2}{4}$ | $y = \frac{x^2}{4}$ | $y = \frac{x^2}{4}$ | $$y = \frac{x^2}{4}$$ |
| Integration (Limits: 1 to 4) | $A = \int_1^4 \frac{x^2}{x} dx$ | $A = \int_1^4 \frac{x^2}{x} dx$ | $$A = \int_1^4 \frac{x^2}{x} dx$$ |
| Differentiation | |||
| First Derivative With Respect To $x$ | $\frac{df}{dx}$ | $\frac{df}{dx}$ | $$\frac{df}{dx}$$ |
| Partial Derivative With Respect To $x$ | $\frac{\partial f}{\partial x}$ | $\frac{\partial f}{\partial x}$ | $$\frac{\partial f}{\partial x}$$ |
| First and Second Derivative of Function | $f\rq$ $f\rq\rq$ | $f\rq$$f\rq\rq$ | $$f\rqf\rq\rq$$ |
| First and Second Derivative With Respect To Time | $\dot f$ $\ddot f$ | $\dot f$$\ddot f$ | $$\dot f\ddot f$$ |
Complex Numbers
| Notation | Example | Inline | Block |
|---|---|---|---|
| Imaginary Unit $i$ | $z=3+2i$ | $z=3+2i$ | $$z=3+2i$$ |
| Real Part Of Complex Number | $\Re(z)=3$ $\operatorname{Re}(z)=3$ | $\Re(z)=3$$\operatorname{Re}(z)=3$ | $$\Re(z)=3\operatorname{Re}(z)=3$$ |
| Imaginary Part Of Complex Number | $\Im(z)=2$ $\operatorname{Im}(z)=2$ | $\Im(z)=2$$\operatorname{Im}(z)=2$ | $$\Im(z)=2\operatorname{Im}(z)=2$$ |
| Complex Conjugate | $\bar{z}=z^*=3-2i$ | $\bar{z}=z^*=3-2i$ | $$\bar{z}=z^*=3-2i$$ |
Greek Alphabet
| Letter | Lower | Inline | Upper | Inline |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alpha | $\alpha$ | $\alpha$ | $\Alpha$ | $\Alpha$ |
| Beta | $\beta$ | $\beta$ | $\Beta$ | $\Beta$ |
| Gamma | $\gamma$ | $\gamma$ | $\Gamma$ | $\Gamma$ |
| Delta | $\delta$ | $\delta$ | $\Delta$ | $\Delta$ |
| Epsilon | $\epsilon$ | $\epsilon$ | $\Epsilon$ | $\Epsilon$ |
| Zeta | $\zeta$ | $\zeta$ | $\Zeta$ | $\Zeta$ |
| Eta | $\eta$ | $\eta$ | $\Eta$ | $\Eta$ |
| Theta | $\theta$ | $\theta$ | $\Theta$ | $\Theta$ |
| Iota | $\iota$ | $\iota$ | $\Iota$ | $\Iota$ |
| Kappa | $\kappa$ | $\kappa$ | $\Kappa$ | $\Kappa$ |
| Lambda | $\lambda$ | $\lambda$ | $\Lambda$ | $\Lambda$ |
| Mu | $\mu$ | $\mu$ | $\Mu$ | $\Mu$ |
| Nu | $\nu$ | $\nu$ | $\Nu$ | $\Nu$ |
| Xi | $\xi$ | $\xi$ | $\Xi$ | $\Xi$ |
| Omicron | $\omicron$ | $\omicron$ | $\Omicron$ | $\Omicron$ |
| Pi | $\pi$ | $\pi$ | $\Pi$ | $\Pi$ |
| Rho | $\rho$ | $\rho$ | $\Rho$ | $\Rho$ |
| Sigma | $\sigma$ | $\sigma$ | $\Sigma$ | $\Sigma$ |
| Tau | $\tau$ | $\tau$ | $\Tau$ | $\Tau$ |
| Upsilon | $\upsilon$ | $\upsilon$ | $\Upsilon$ | $\Upsilon$ |
| Phi | $\phi$ | $\phi$ | $\Phi$ | $\Phi$ |
| Chi | $\chi$ | $\chi$ | $\Chi$ | $\Chi$ |
| Psi | $\psi$ | $\psi$ | $\Psi$ | $\Psi$ |
| Omega | $\omega$ | $\omega$ | $\Omega$ | $\Omega$ |
History Of Adding Math Notation To Markdown Documents
LaTeX is sometimes stylised as $\LaTeX$. Typesetting is based on $\TeX$, created by Donald Knuth .
Open source editor, VSCode, supports math typesetting with $\LaTeX$, showing the notation as you type. The Live Preview Pane is enabled with Ctrl + K V. No other libraries, extensions or apps need to be installed. Rendering in Live Preview is performed by KaTeX , a fast, easy-to-use JavaScript library for $\TeX$ math rendering on the web.